Research
Dr. Khaled Omar Sebakhy is currently an assistant professor of chemical engineering in Bahrain polytechnic, Kingdom of Bahrain. His research expertise lies in chemical engineering, materials chemistry, and polymer chemistry. His current work focuses on the synthesis of bio-based and sustainable polymers through environmentally friendly approaches and green pathways. His research bridges the gap between Green chemistry, polymer science and nanotechnology.
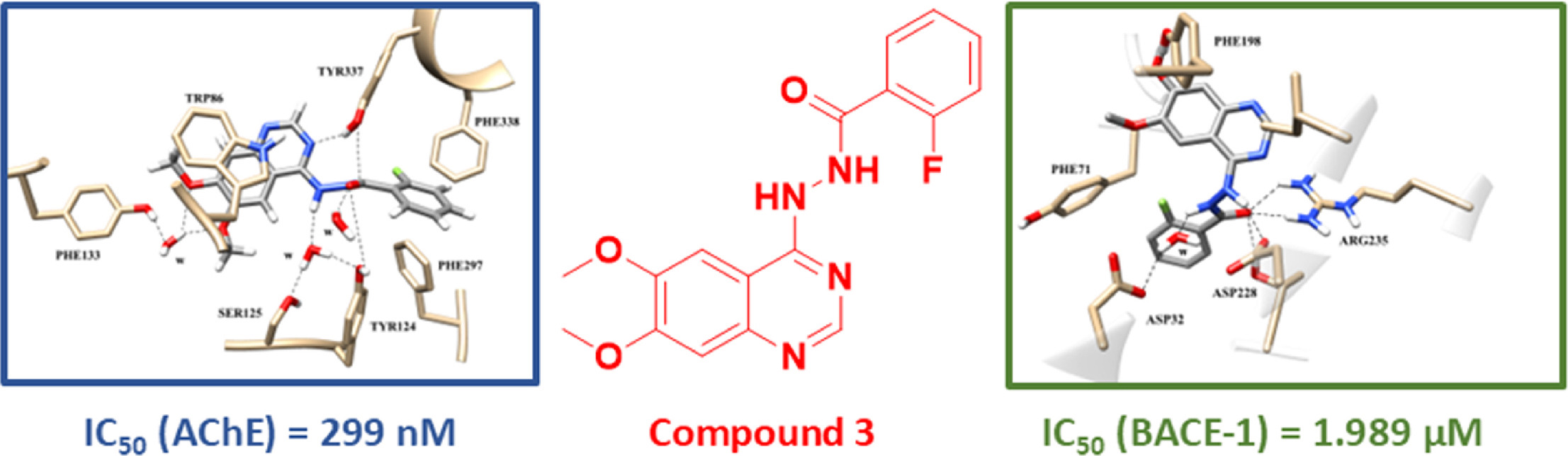
Discovery of 6,7-Dimethoxyquinazoline-Hydrazide Hybrids as Dual Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and β-Secretase.
A novel series of 6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline-hydrazide hybrids 1-4 were designed, synthesized, and tested for their AChE inhibition activity using the qualitative assay, which showed that compounds 3 and 4 exhibited their activity via TLC. The compounds were characterized using HRMS, IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Further in vitro AChE and BACE-1 inhibition activities of both derivatives (3 and 4) revealed that compound 3 exhibited outstanding inhibitory activity against AChE, with IC50 of 299 nM, in comparison to the reference standard, rivastigmine (IC50 of 439 nM). Moreover, the same derivative showed inhibitory activity against BACE-1 with IC50 of 1.989 μM, superior to the standard control, quercetin (IC50 of 4.55 μM). Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed the stability of the AChE- and BACE-1-compound 3 complexes, with both systems reaching equilibrium within the first 25 ns and maintaining low RMSD values thereafter. Post-equilibration analyses revealed stable binding modes supported by key hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions within the active sites. These findings highlight compound 3's strong affinity and specificity toward both targets, supporting its potential as a dual inhibitor.
Solution viscosity and ion-specific crosslinking govern structure of alginate and pectin hydrogels: Correlating solid-state NMR with rheology.
Hydrogels are widely utilized in biomedical, food, and pharmaceutical applications, where their functionality depends critically on their tunable mechanical and dynamic properties. These properties are governed by the solution viscosity and the nature of ionic crosslinking within their constituent polymers.
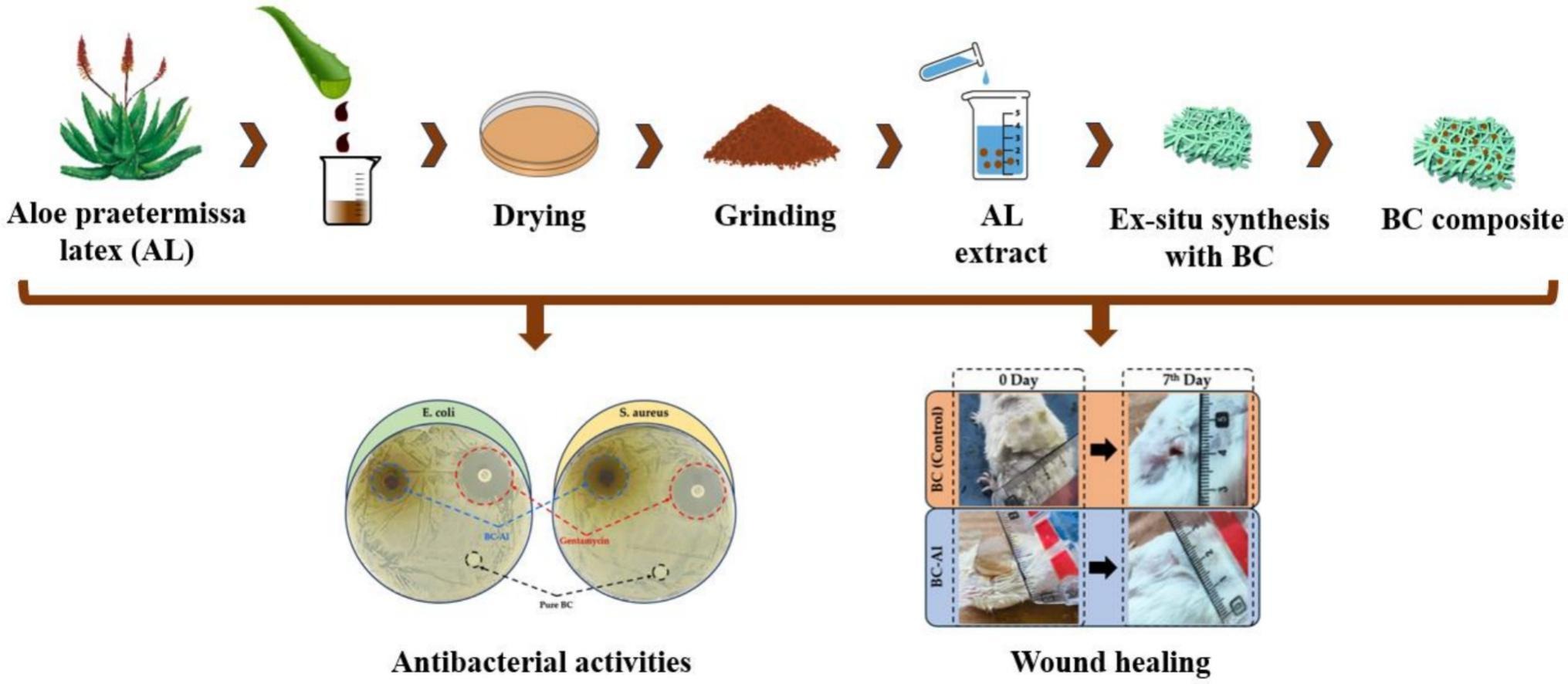
Bacterial cellulose–Aloe praetermissa hydrogels for enhanced antibacterial and biocompatible wound care
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is a superior biopolymer for wound healing due to its high water-holding ability, exceptional biocompatibility, and extracellular matrix-like structure. However, its therapeutic efficacy is limited by its lack of inherent antimicrobial activity.
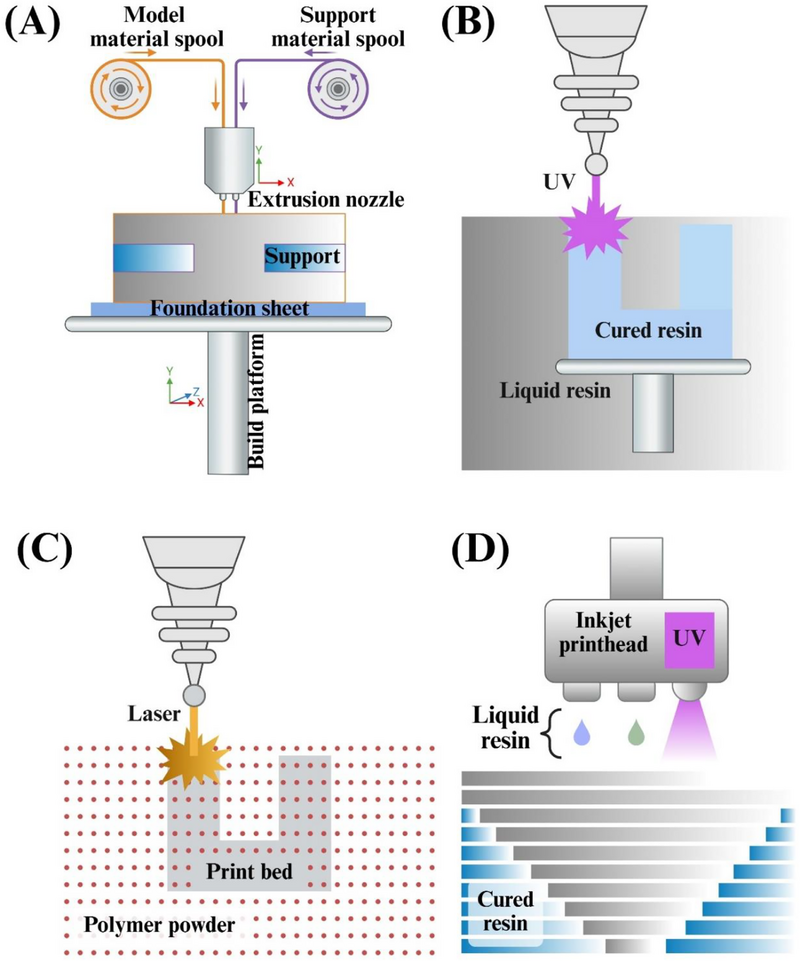
From Bioinks to Functional Tissues and Organs: Advances, Challenges, and the Promise of 3D Bioprinting
3D printing, particularly bioprinting, has emerged as a transformative technology in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, enabling the precise layer‐by‐layer fabrication of living tissues and complex biomaterials. Bioprinting has evolved through advances in printing methods such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), powder bed fusion (PBF), and jetting techniques, each offering distinct advantages for producing high‐resolution, functional constructs.
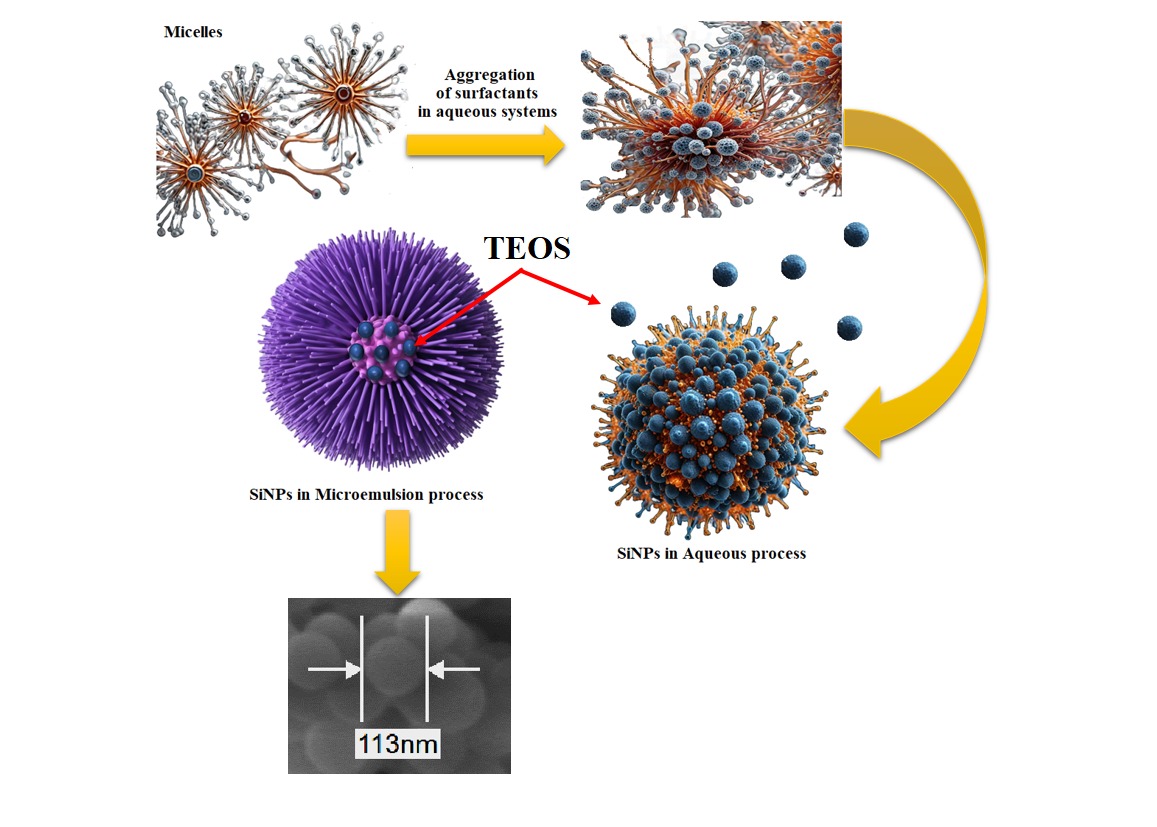
Synthesis of shape‐controlled silica nanoparticles via dual soft templates: A comparative study between aqueous and microemulsion synthesis for the impregnation of procaine …
Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) are promising drug delivery nanocarriers due to their tunable size, porous structure, and surface properties. This study compares two synthesis methods: (i) a low‐temperature aqueous sol–gel process yielding SiNPs of 500–700 nm, and (ii) a water‐in‐oil (W/O) microemulsion using either CTAB or TX‐100 surfactants. Surfactant selection significantly affected nanoparticle size, stability, and dispersity. Characterization by dynamic light scattering (DLS)...
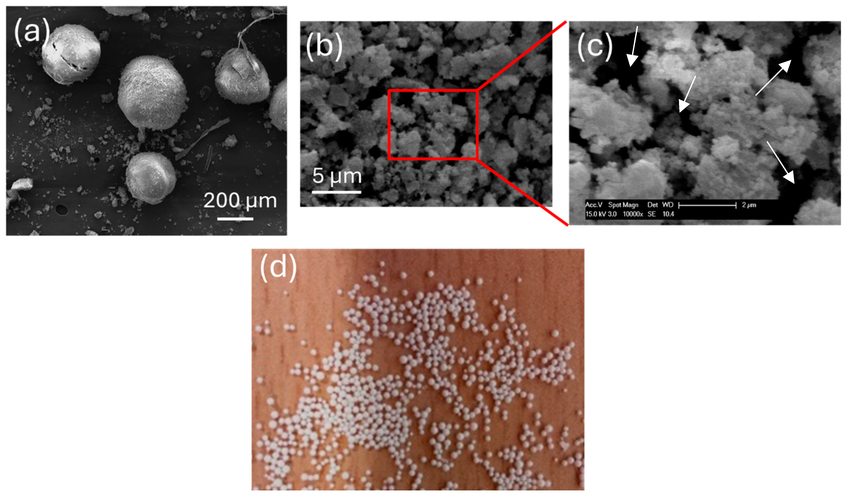
Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates
In this study, the effects of several synthesis parameters including aging time, micropore-structure-directing agents, and hydrothermal treatment temperature profile were systematically examined with respect to their impact on the crystallinity of macroscopic zeolite Y spheres formed in the presence of organic anion-exchange resin templates. Spherical resins were utilized as hard templates to shape the zeolite Y particles.
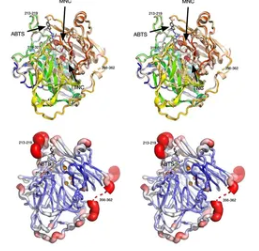
Polymerization potential of a bacterial CotA-laccase for β-naphthol: enzyme structure and comprehensive polymer characterization
Laccases are blue-multicopper containing enzymes that are known to play a role in the bioconversion of recalcitrant compounds. Their role in free radical polymerization of aromatic compounds for their valorization remains underexplored. In this study, we used a pBAD plasmid containing a previously characterized CotA laccase gene (abbreviated as Bli-Lacc) from Bacillus licheniformis strain ATCC 9945a to express this enzyme and explore its biotransformation/polymerization potential on β-naphthol.
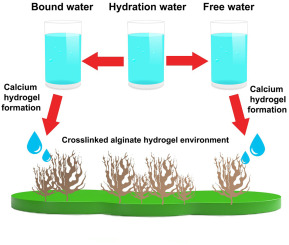
A comparative analytical study for the different water pools present in alginate hydrogels: Qualitative vs. quantitative approaches
Alginate hydrogels have garnered significant attention due to their promising applications in the food, biomedical, and pharmaceutical industries. The detection and quantification of distinct water phases within these hydrogels offer valuable insights into their dynamic, absorptive, and mechanical properties. Despite being comprised solely of 2 wt. % polymeric materials, the alginate hydrogels exhibit a highly porous morphology, characterized by distinct water pools exhibiting varying mobility and dynamic behaviors.
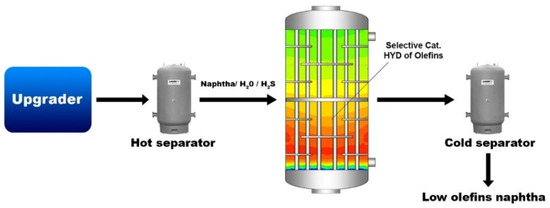
Enhanced Catalytic Hydrogenation of Olefins in Sulfur-Rich Naphtha Using Molybdenum Carbide Supported on γ-Al2O3 Spheres under Steam Conditions …
Spheres comprising 10 wt.% Mo2C/γ-Al2O3, synthesized through the sucrose route, exhibited unprecedented catalytic activity for olefin hydrogenation within an industrial naphtha feedstock that contained 23 wt.% olefins, as determined by supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC). The catalyst demonstrated resilience to sulfur, exhibiting no discernible deactivation signs over a tested 96 h operational period.
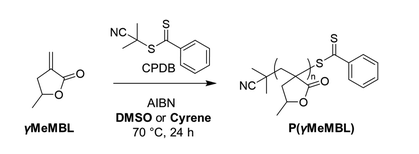
RAFT solution polymerisation of bio-based γ-methyl-α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone monomer in DMSO and Cyrene
Reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) solution polymerisation of the bio-based lactone monomer γ-methyl-α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone (γMeMBL) has been demonstrated in DMSO and Cyrene. RAFT control was evidenced by control over molecular weights, low disperisites, and kinetic evaluation. Purified P(γMeMBL) homopolymers exhibited high glass transition temperatures (206–221 °C) and excellent thermal stabilities.
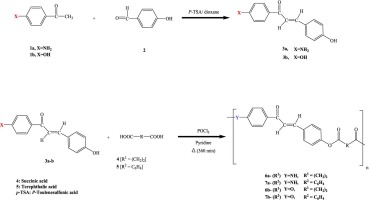
Molecular conjugation and crystallinity impact of designed novel chalcone based polyesters and polyesteramides on their thermal-electrical conductivity
Two polyesteramides were synthesized via polycondensation reactions involving 4′-amino-4-hydroxychalcone 3a with succinic acid (4) and terephthalic acid (5), utilizing phosphoryl chloride as a chlorinating agent. A parallel reaction with (E)-1,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one chalcone (3b) yielded two polyesters under identical conditions. The resultant polymers were obtained with excellent yields ranging from 93 % to 98 %.
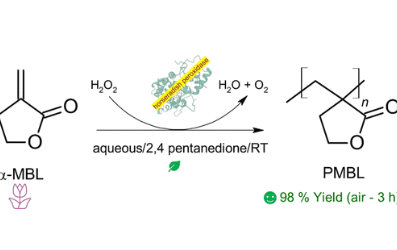
Surfactant-free peroxidase-mediated enzymatic polymerization of a biorenewable butyrolactone monomer via a green approach: Synthesis of sustainable biobased latexes
A green surfactant-free one-pot horseradish peroxidase-mediated enzymatic polymerization is successfully applied to produce a sustainable and thermally stable biobased high average molar mass poly(α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) (PMBL) at ambient conditions in water for the first time.
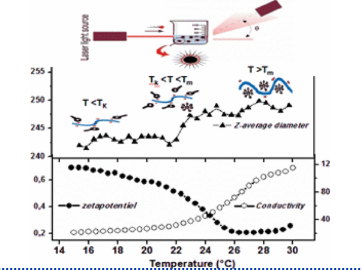
Insights into the characterization of the self-assembly of different types of amphiphilic molecules using dynamic light scattering
The self-assembly of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, sodium dodecylsulfate, Triton X-100, and sulfobetaine surfactants in aqueous solutions was examined by dynamic light scattering, both in the presence and absence of 0.1 M NaCl salt, across various temperatures. For each surfactant, critical parameters, such as concentration and phase transition temperatures, of micelles were determined by monitoring changes in the hydrodynamic diameter with concentration and temperature.
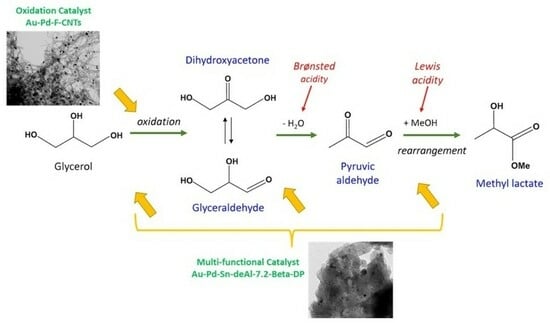
Synergistic catalytic effects of alloys of noble metal nanoparticles supported on two different supports: Crystalline zeolite Sn-Beta and carbon nanotubes for glycerol …
Two multifunctional catalytic systems comprising Sn-based/doped crystalline zeolite Beta were synthesized, and they were employed as heterogeneous catalysts in the selective conversion of glycerol to methyl lactate. The first catalytic system, named Au-Pd-Sn-deAl-7.2-Beta-DP, was created through the post-synthesis dealumination of the parent zeolite Beta (Si/Al = 10) using 7.2 M HNO3.
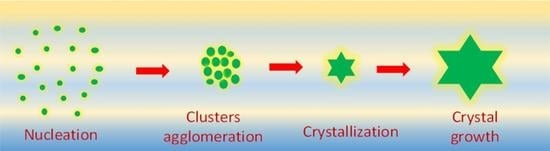
A survey on zeolite synthesis and the crystallization process: Mechanism of nucleation and growth steps
Zeolites, as a class of crystalline minerals, find a wide range of applications in various fields, such as catalysis, separation, and adsorption. More recently, these materials have also been developed for advanced applications, such as gas storage, medical applications, magnetic adsorption, and zeolitic-polymeric membranes. To effectively design zeolites for such intriguing applications, it is crucial to intelligently adjust their crystal size, morphology, and defect population in relation to crystal perfection.
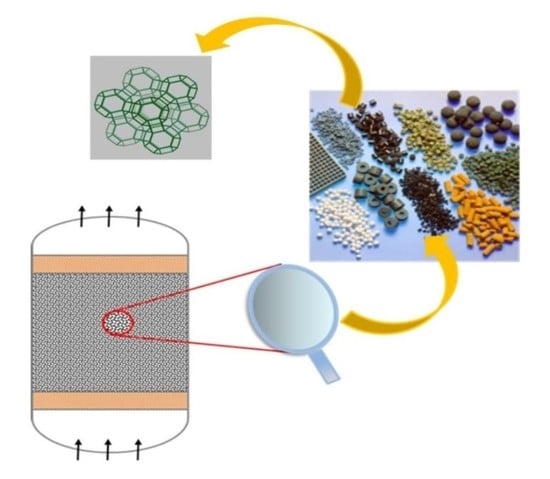
A comparative review of binder-containing extrusion and alternative shaping techniques for structuring of zeolites into different geometrical bodies
Zeolites are crystalline metallosilicates displaying unique physicochemical properties with widespread applications in catalysis, adsorption, and separation. They are generally obtained by a multi-step process that starts with primary mixture aging, followed by hydrothermal crystallization, washing, drying, and, finally, a calcination step.
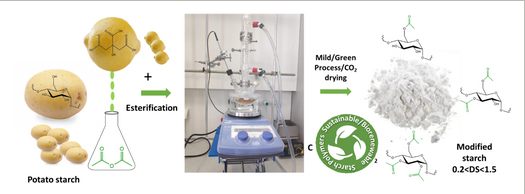
A green/sustainable organocatalytic pathway for the preparation of esterified supercritical CO2‐dried potato starch products
Production of renewable and modified starch‐based products was achieved using a sustainable catalyst and an environmentally friendly drying process via supercritical CO2. Potato starch was modified via a sustainable and green esterification process with acetic anhydride reagent implementing a novel organocatalytic pathway at different periods of time (0.5, 3 and 7 h) by applying an esterification reaction at 120°C targeting
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy: Towards structural insights into starch-based materials in the food industry
Solid-state NMR is a nondestructive and noninvasive technique used to study the chemical structure and dynamics of starch-based materials and to bridge the gap between structure–function relationships and industrial applications. The study of crystallinity, chemical modification, product blending, molecular packing, amylose–amylopectin ratio, end chain motion, and solvent–matrix interactions is essential for tailoring starch product properties to various applications.

Binder‐free Zeolite Beta Beads with Hierarchical Porosity: Synthesis and Application as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Anisole Acylation
Three zeolites (H‐Beta, H‐ZSM‐5 and H‐Y) were synthesized in the form of binder‐free macroscopic beads (d=215–840 μm) using a hydrothermal method employing anion‐exchange resin beads as hard template. The beads obtained after removal of the hard template by calcination consisted of crystalline zeolite domains connected with each other to form a hierarchical porous network
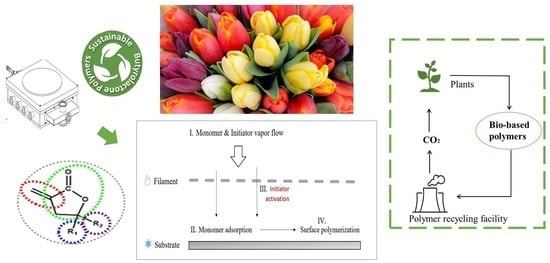
Initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) of bio-based poly (tulipalin A) coatings: structure and material properties
A solvent-free route of initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) was used to synthesize a bio-renewable poly(α-Methylene-γ-butyrolactone) (PMBL) polymer. α-MBL, also known as tulipalin A, is a bio-based monomer that can be a sustainable alternative to produce polymer coatings with interesting material properties. The produced polymers were deposited as thin films on three different types of substrates—polycarbonate (PC) sheets, microscopic glass, and silicon wafers—and characterized via an array of characterization techniques,
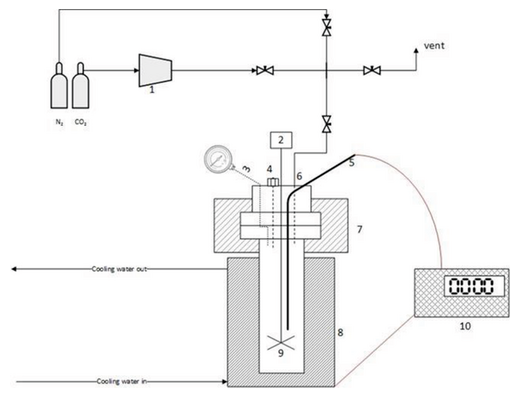
RAFT polymerization of a biorenewable/sustainable monomer via a green process
A biorenewable polymer is synthesized via a green process using the RAFT principle for the first time in supercritical CO2 at 300 bar and 80 °C. α‐Methylene‐γ‐butyrolactone polymers of various chain lengths and molecular weights are obtained. The molecular weights vary from 10 000 up to 20 000 with low polydispersity indexes .

A study on the characteristics of Algerian Hassi-Messaoud asphaltenes: Solubility and precipitation
This study focuses on detailed characterizations of asphaltene fractions extracted from the Algerian Hassi-Messaoud oil field. It was found that the extracted asphaltenes are not completely soluble in toluene, instead two fractions of asphaltenes were obtained upon solubilizing the heptane-precipitated neat asphaltenes in toluene.
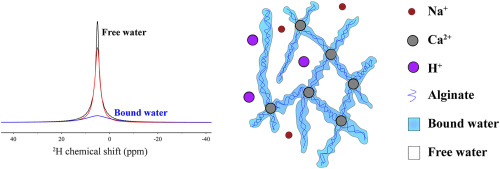
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy insights for resolving different water pools in alginate hydrogels
Alginate hydrogels are versatile self-assembling biocompatible materials with diverse biomedical and food industrial applications, which includes uses in encapsulation, (drug) delivery and tissue engineering. Hydrogel formation requires cross-linking, which for alginates is often done with calcium ions that engage in specific interactions with the polysaccharide carboxylic acid groups.
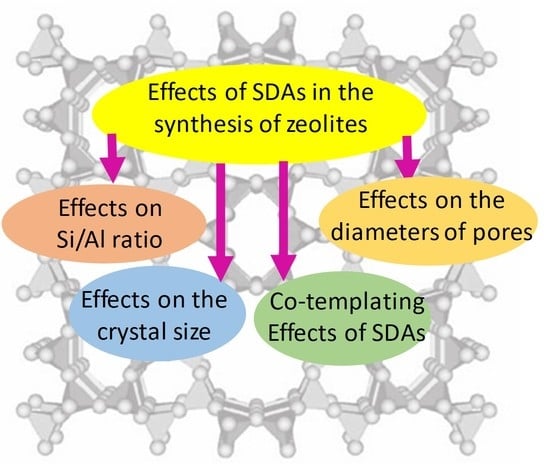
A review on the effects of organic structure-directing agents on the hydrothermal synthesis and physicochemical properties of zeolites
The study on the synthesis of zeolites, including both the development of novel techniques of synthesis and the discovery of new zeolitic frameworks, has a background of several decades. In this context, the application of organic structure-directing agents (SDAs) is one of the key factors having an important role in the formation of porous zeolitic networks as well as the crystallization process of zeolites.
Solid state NMR a powerful technique for investigating sustainable/renewable cellulose-based materials
Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (ssNMR) is a powerful and attractive characterization method for obtaining insights into the chemical structure and dynamics of a wide range of materials. Current interest in cellulose-based materials, as sustainable and renewable natural polymer products, requires deep investigation and analysis of the chemical structure, molecular packing,
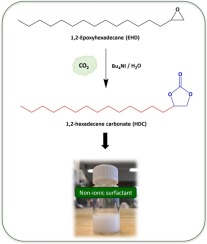
Novel non-ionic surfactants synthesised through the reaction of CO2 with long alkyl chain epoxides
Two long alkyl chain cyclic carbonates, 1,2-hexadecene carbonate (HDC) and 1,2-dodecene carbonate (DDC), were synthesised via a green catalytic approach from CO2 and the corresponding epoxide, achieving nearly complete conversion with full selectivity.
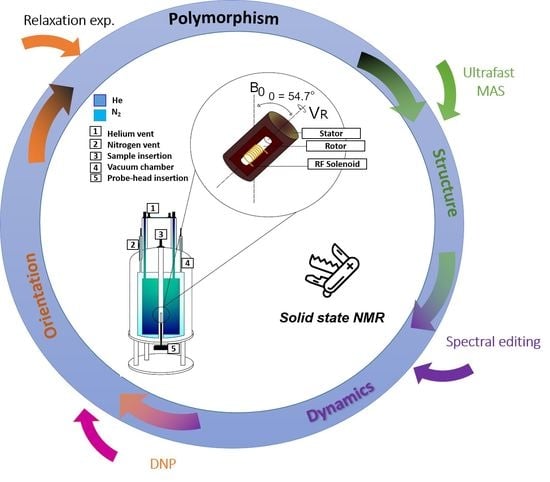
Solid state nmr spectroscopy a valuable technique for structural insights of advanced thin film materials: A review
Solid-state NMR has proven to be a versatile technique for studying the chemical structure, 3D structure and dynamics of all sorts of chemical compounds. In nanotechnology and particularly in thin films, the study of chemical modification, molecular packing, end chain motion, distance determination and solvent-matrix interactions is essential for controlling the final product properties and applications.
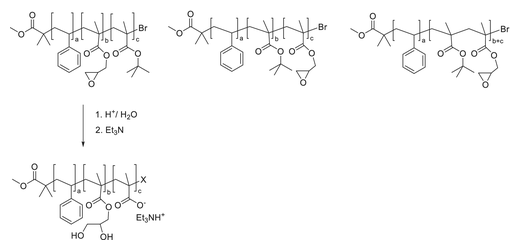
Design and synthesis of novel di‐and triblock amphiphilic polyelectrolytes: Improving salt‐induced viscosity reduction of water solutions for potential application in enhanced …
In the present study, three different block copolymers based on styrene, tert‐butyl methacrylate, and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) were synthesized via sequential atom transfer radical polymerization. The addition of the GMA block was found to be best performed at 60°C.
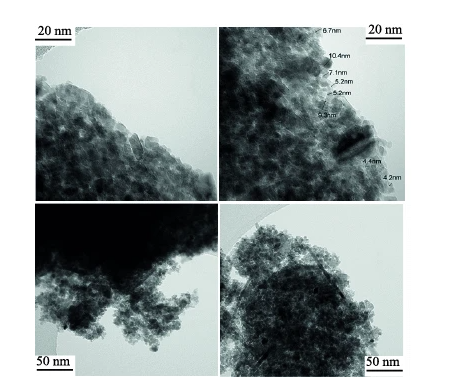
Adsorption of Algerian asphaltenes onto synthesized maghemite iron oxide nanoparticles
In this study, the adsorption of Algerian asphaltene sample extracted from Hassi Messaoud oil field is conducted for the first time. The adsorption process was performed using novel synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3). γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles were in-house synthesized and characterized by an array of techniques using, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
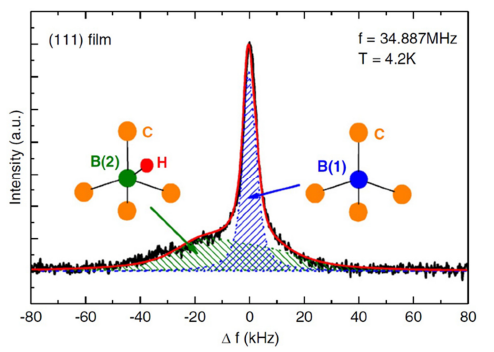
Solid State NMR Spectroscopy a Valuable Technique for Structural Insights of Advanced Thin Film Materials: A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1494
Solid-state NMR has proven to be a versatile technique for studying the chemical structure, 3D structure and dynamics of all sorts of chemical compounds. In nanotechnology and particularly in thin films, the study of chemical modification, molecular packing, end chain motion, distance determination and solvent-matrix interactions is essential for controlling the final product properties and applications.

Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR) Methodology for Monolefin Analysis: Application to Aquaprocessing-Upgraded Bitumen
Olefins are problematic components of petroleum products responsible for gum formation, polymers, and solid deposition in oil facilities. This work presents a methodology developed for monolefin analysis of whole oils, diluted bitumen, and partially upgraded heavy oils.
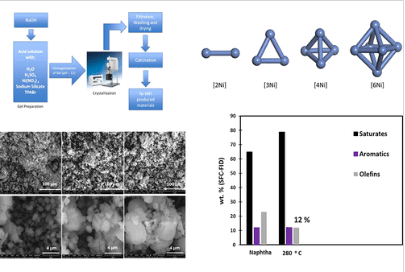
Production of highly dispersed Ni within nickel silicate materials with the MFI structure for the selective hydrogenation of olefins
Aluminum-free Ni-incorporated MFI zeolite materials were synthesized in a batch reactor under mild reaction conditions using the hydrothermal method and were proven to exhibit highly active sites for the saturation of aromatics and olefinic molecules due to the high dispersion of the Ni species.
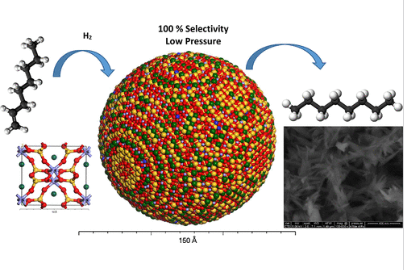
Dispersed Ni-doped aegirine nanocatalysts for the selective hydrogenation of olefinic molecules
A mild hydrothermal route was employed for the first time to prepare pure synthetic aegirine nanocatalysts with high dispersion of the nickel species, different Ni contents, low-temperature reducibility of the Ni2+ species, and two average nanocrystalline domain sizes of 12 and 25 nm.
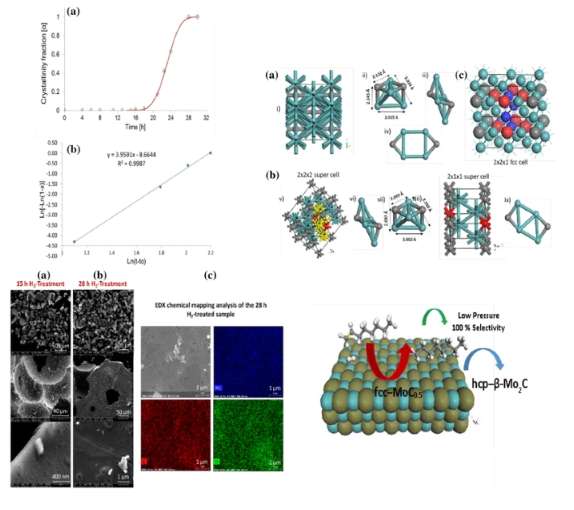
New insights into the kinetics of structural transformation and hydrogenation activity of nano-crystalline molybdenum carbide
Transformation of cubic molybdenum carbide into hexagonal β-Mo2C was found to follow the Avrami–Erofeev kinetic model with an n parameter of four indicating a slow nucleation step with a polyhedral growth of the transformed phase. The transformation not only occurred at 773 K under atmospheric H2 pressure, but also imperceptibly occurred under the employed hydrogenation reaction conditions
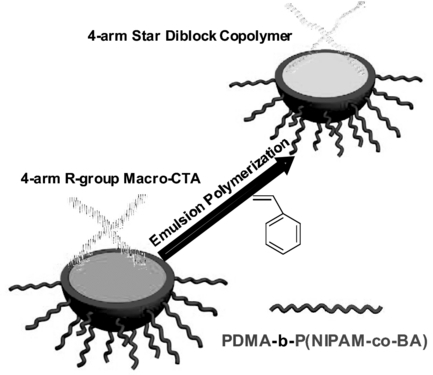
Nanoparticles of Well‐Defined 4‐Arm Stars made using Nanoreactors in Water
n this work, the use of a nanoreactor is demonstrated to rapidly prepare monodisperse polymer nanoparticles in water‐based dispersion consisting of 4‐arm star polymer via the R‐group RAFT approach. It is shown that by heating a nanoparticle assembler above its lower critical solution temperature (LCST), stabilized nanoparticles are formed that act as a template for the 4‐arm star RAFT‐mediated polymerization of styrene.
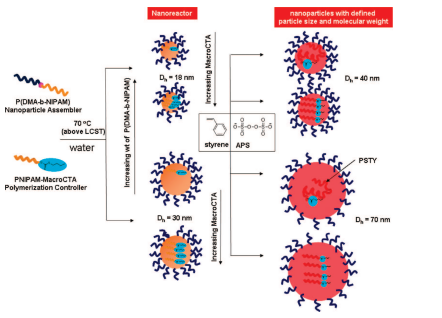
Nanoreactors to synthesize well-defined polymer nanoparticles: decoupling particle size from molecular weight
Considerable attention has been directed toward the synthesis of polymer nanoparticles via reversible additionrfragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) in an dispersed aqueous medium (eg, emulsion, miniemulsion). 1r5 The major advantages of performing polymerizations in dispersed aqueous media over bulk or solution include the following: